CEIBS releases carbon disclosure report
September 15, 2023. Shanghai –In response to China’s dual carbon targets and green energy efforts, CEIBS launched comprehensive carbon neutrality endeavors in 2023, after conducting greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories in both 2019 and 2021. Drawing on insights from these inventories, CEIBS is now ready to debut our Carbon Information Disclosure Report in order to offer a detailed account of our GHG emissions and progress in carbon reduction measures across our five campuses, demonstrating our unwavering commitment to achieving carbon neutrality.
The report shows that CEIBS has made substantial progress in emission reduction, with GHG emissions decreasing by 4.63% in 2021 compared to 2019. It also outlines CEIBS' carbon neutrality goals for the future, highlighting concrete steps and a medium-to-long-term action plan for achieving Scopes 1 and 2 carbon neutrality by 2035 and full-scope carbon neutrality by 2050.
Substantial decrease in carbon emissions
CEIBS reports a 4.63% GHG emission decrease in 2021
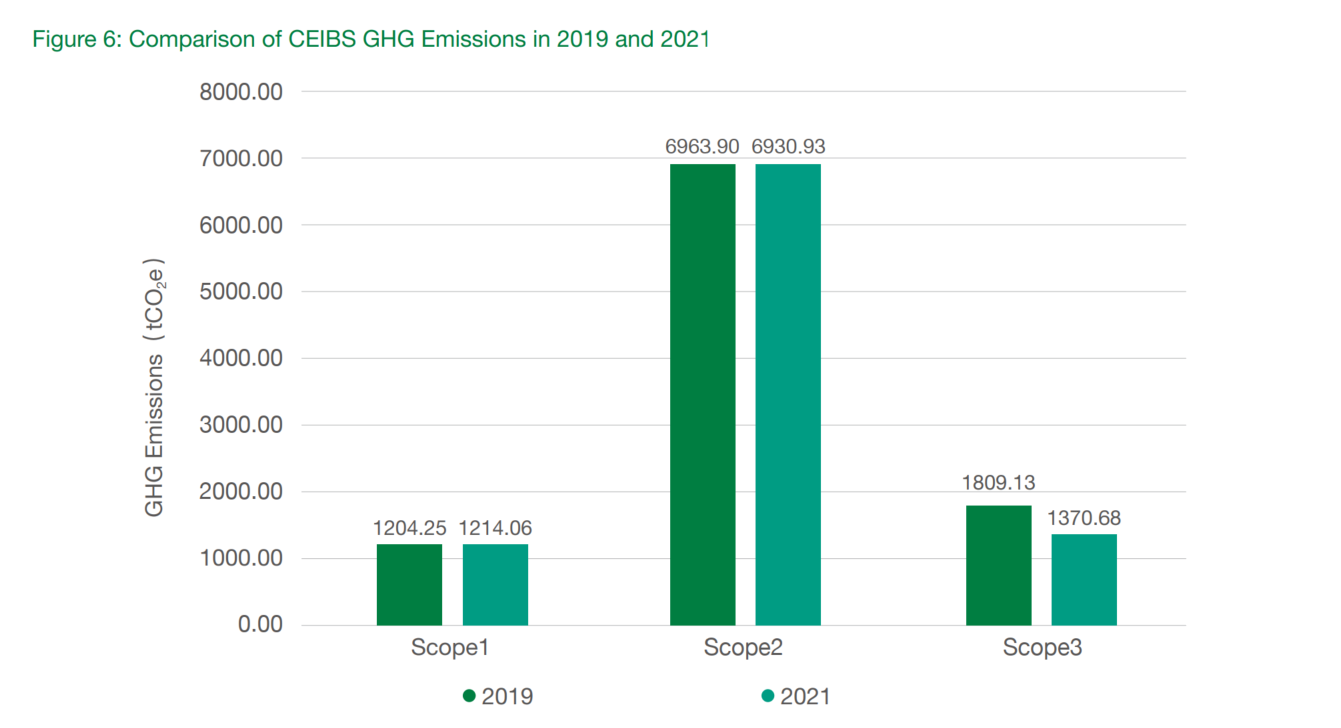
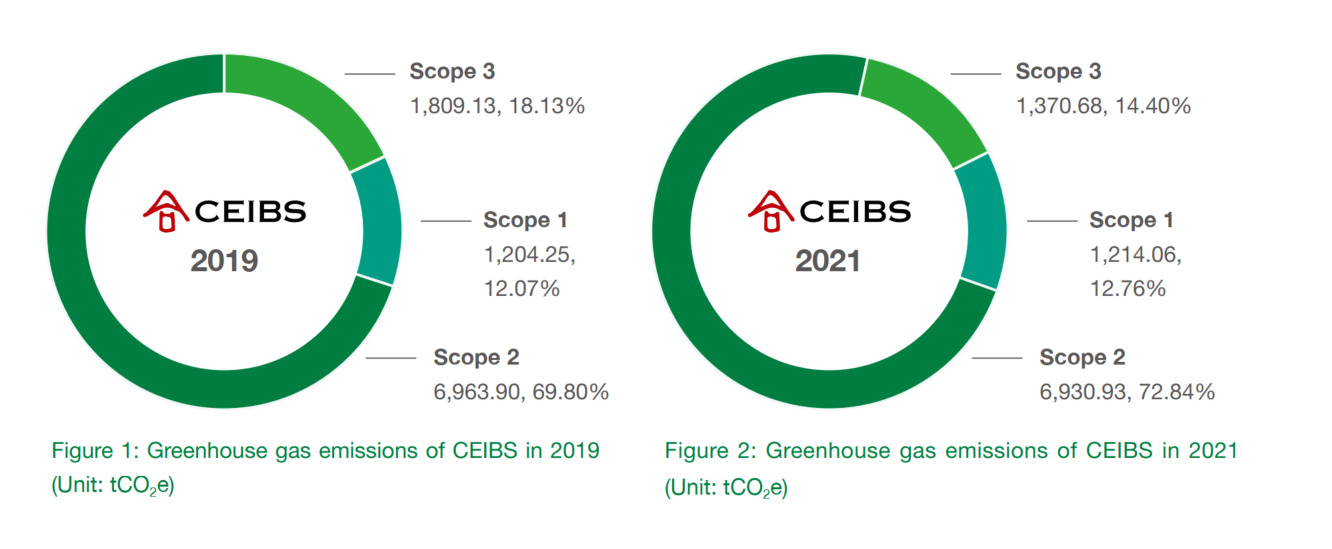
In 2021, total emissions across the five CEIBS campuses amounted to 9,515.13 tCO2e, down from 9,977.29 tCO2e in 2019, representing a 4.63% reduction in the last four years.
GHG Emissions: 2019 vs. 2021
CEIBS’ 2019 and 2021 GHG emission inventories involved the following three scopes:
Scope 1
Direct GHG emissions, including stationary combustion, mobile combustion, and fugitive emissions.
Scope 2
Indirect emissions from imported energy sources, including purchased electricity, which refers to GHG emissions generated from purchased electricity within the organizational boundary.
Scope 3
Indirect emissions generated by the upstream and downstream supply chain resulting from employee commuting, business travel, purchased paper, and waste disposal.
Emissions decline most significantly in Scope 3
Among the three scopes examined, Scope 3 exhibited the most significant reduction in GHG emissions.
Compared to 2019, data from 2021 indicated that Scope 1 emissions had increased by 9.81 tCO2e, driven by an increase in fugitive greenhouse gas emissions from refrigerants and fire extinguishers.
Scope 2 emissions decreased by 32.97 tCO2e, as CEIBS increased its number of offline courses and activities, particularly a certain amount of concentrated courses on the Shanghai campus. Meanwhile, grid emission factors in our China, Switzerland, and Ghana campuses all decreased in 2021 compared to 2019. These two factors together resulted in a slight decrease in total greenhouse gas emissions from purchased electricity in CEIBS in 2021.
In comparison, Scope 3 emissions fell by 32% to 438.45 tCO2e, largely due to reduced travel activities in 2021. With the gradual recovery of personnel activities and the improvement of statistical accuracy of Scope 3 data on offer in coming years, we will make a dedicated effort to present Scope 3 emissions more comprehensively in future reports.
Carbon emissions in three scopes
CEIBS low-carbon action plan
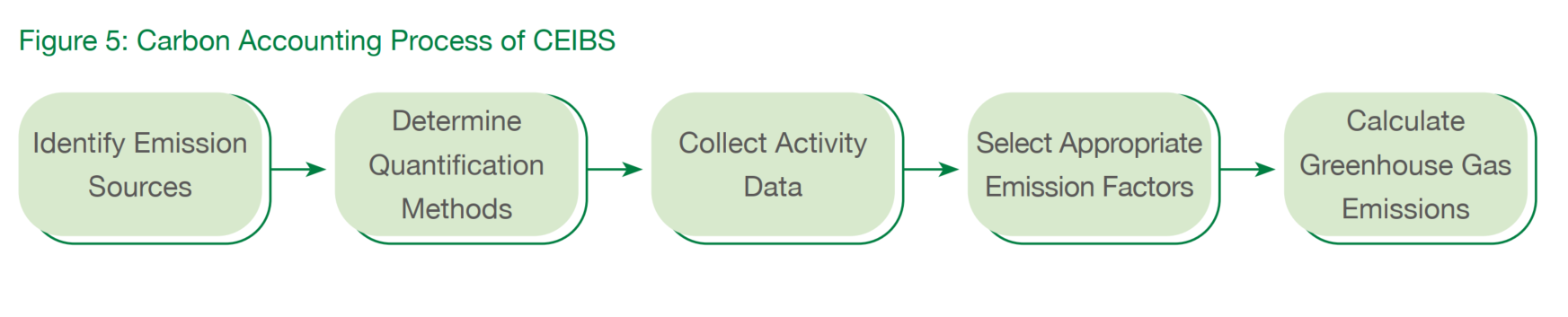
Each carbon inventory followed the following five steps:
Carbon neutrality through low-carbon, energy-efficient construction
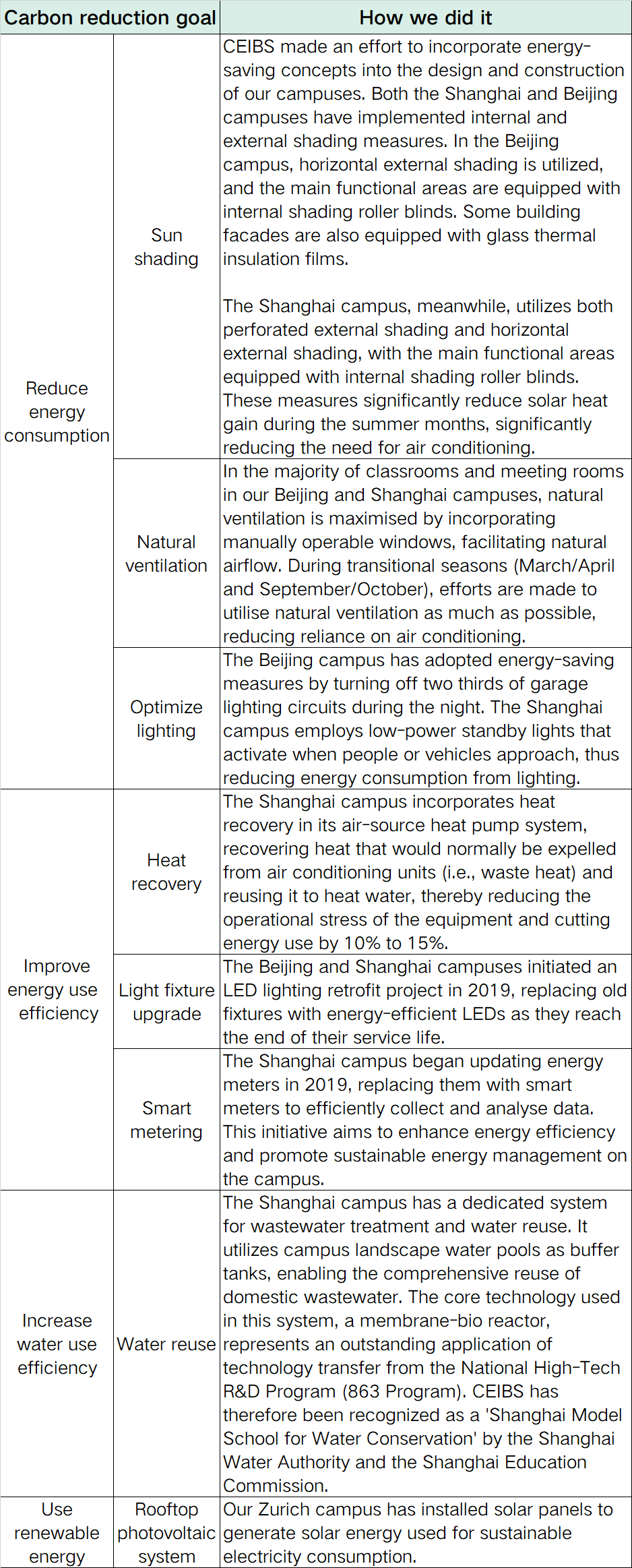
Since its establishment, CEIBS has been actively committed to running a green campus. Building low-carbon and energy-efficient campus buildings is a key pillar of our strategy for achieving carbon neutrality. In 2013, the CEIBS student dormitories and Shanghai campus (Phase 3) were awarded the Gold Certification of Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design (LEED), recognizing CEIBS' initiatives in green construction and environmentally friendly design. In 2022, CEIBS Shanghai campus initiated the ‘Smart Campus’ project, paving the way for more sustainable energy consumption efforts in the future.
CEIBS has also made notable progress in reducing energy consumption, improving water and energy efficiency, and adopting renewable energy. Key measures for energy savings and carbon reduction are outlined in the table below.
How can we build on our successes & achieve more in the future?
CEIBS believes in the power of small steps to lead to significant progress. To this end, we will continue to elevate our carbon management capabilities and reduce our carbon footprint through comprehensive carbon reduction actions. We will also bolster collaboration and communication with various stakeholders to jointly advance carbon reduction initiatives and mitigate climate risks. Our goal is to create a new development paradigm by synergizing talent development, cultural exchange, and green, low-carbon initiatives, collectively forging a sustainable and low-carbon future.
Our commitment to carbon neutrality
CEIBS is committed to achieving Scope 1 and 2 carbon neutrality by 2035 and full-scope carbon neutrality by 2050. This crucial decision is informed by meticulous assessments of GHG emissions, forecasts of carbon reduction pathways, and a reliable evaluation of the feasibility of our carbon reduction measures.
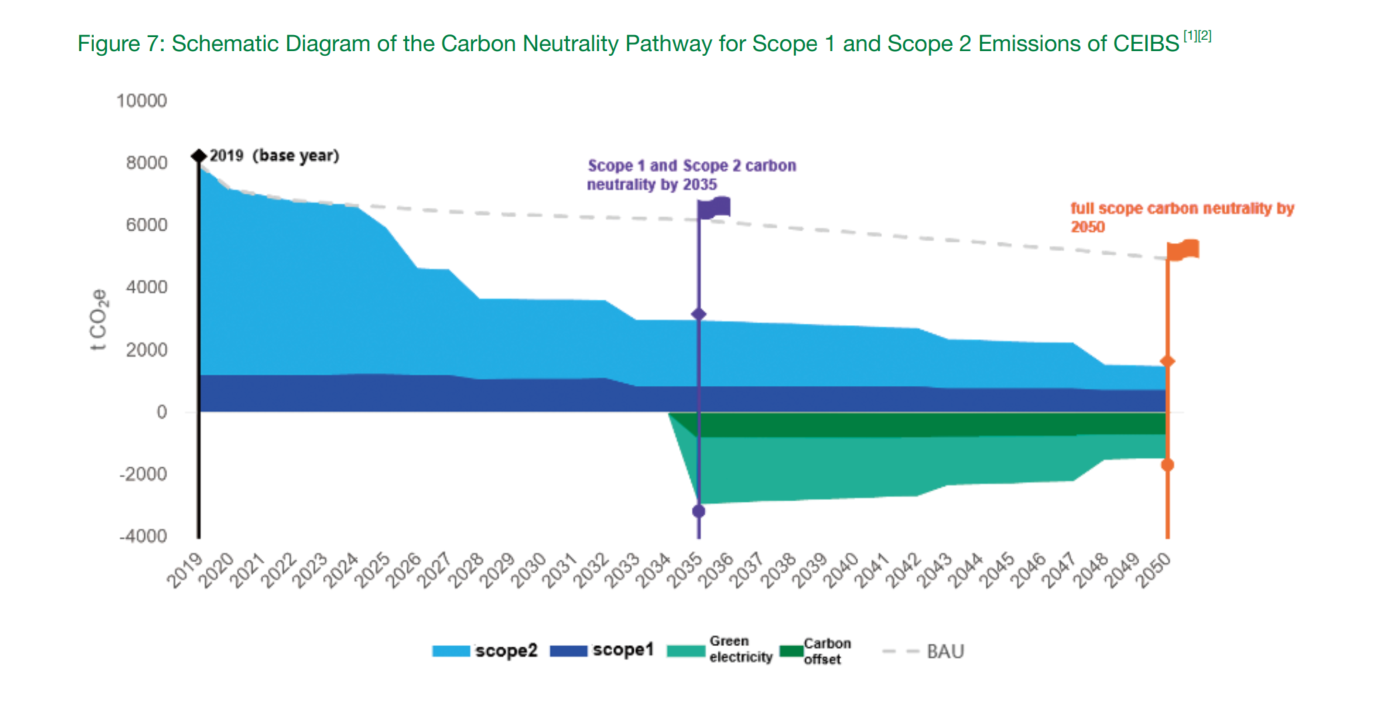
Note: The Shenzhen campus is relocating and not included in the carbon neutrality pathways.
Three-year action plan (2024—2026)
Over the next three years, CEIBS will build upon its existing strategies and, as appropriate to local conditions and timing, prioritise a range of carbon reduction initiatives with a particular emphasis on our Beijing and Shanghai campuses. At the same, the school will also advance carbon reduction efforts across all five of our campuses. The detailed action plan is outlined below.
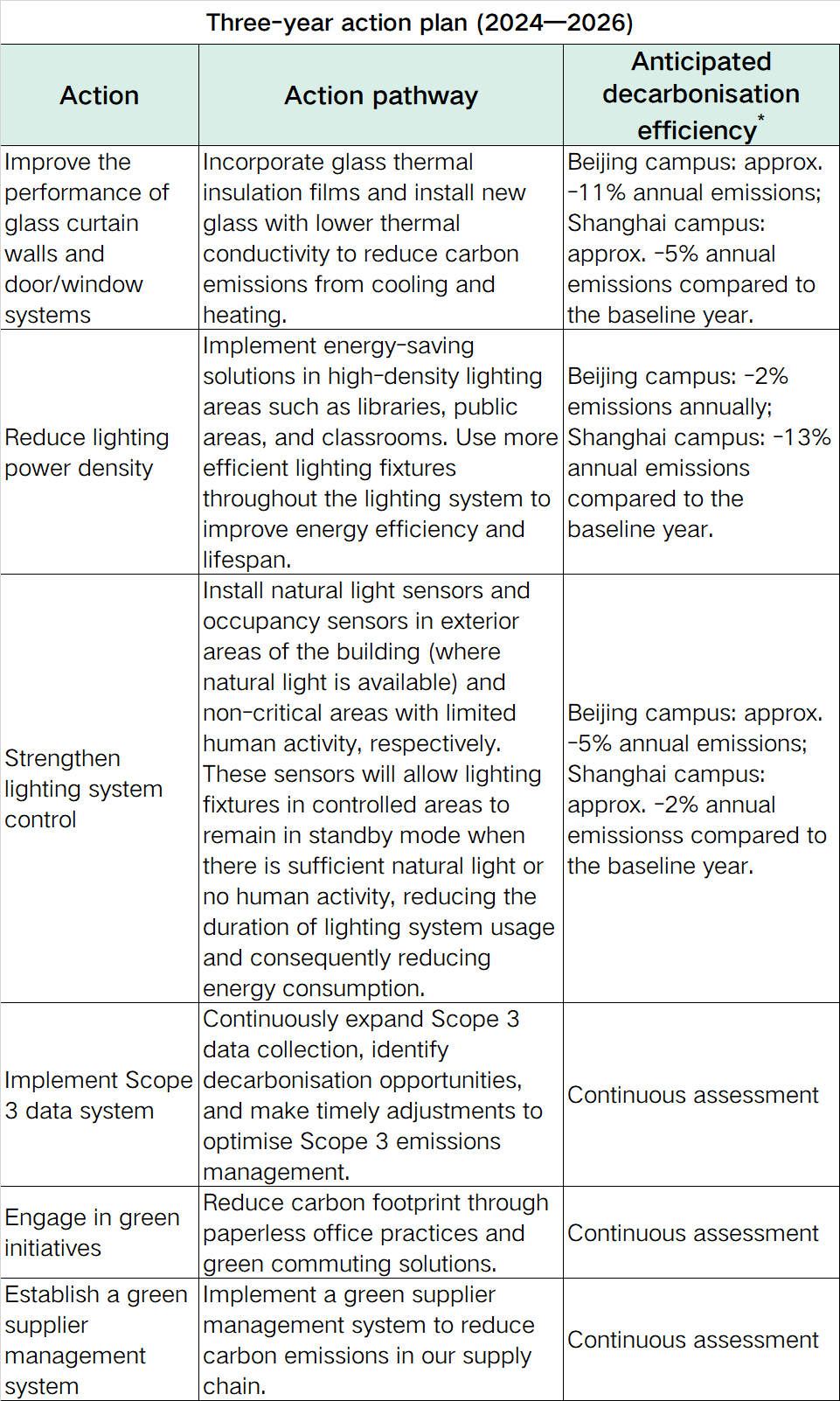
* Note: Reduction in carbon emissions is calculated based on the assumption that all engineering projects have been fully implemented.
Based on a multidimensional analysis of actual needs, decarbonisation potential, and economic benefits, CEIBS has developed short-term (three-year), medium-term, and long-term action plans to achieve carbon neutrality.
In terms of engineering measures, efforts will be made to reduce energy demand, enhance efficiency, and promote the use of renewable energy. This includes reducing energy losses in existing campus buildings through maintenance and upgrading of heat-insulating films and insulation materials, improving efficiency in major energy-consuming systems like electrical and HVAC equipment, and harnessing renewable energy sources such as rooftop solar panels to minimize in-house emissions.
On the management front, CEIBS will implement a series of plans to recycle resources and significantly reduce carbon emissions, especially regarding Scope 3 emissions. These include promoting green commuting (e.g., high-speed rail, subway, and public transportation), paperless offices, textbook recycling, responsible procurement and investment, and internal carbon pricing.
Moreover, we will upgrade our energy management system by integrating smart campus data and capturing detailed information on various energy consumption metrics to enable regular tracking of energy efficiency indicators and in-depth analysis of energy consumption comparisons. This will help us assess the effectiveness of various measures and make regular optimisations and adjustments to our action plans.
Beyond these proactive efforts, CEIBS will also expand our low-carbon influence and strengthen the promotion of green and low-carbon awareness and education by offering more ESG courses, conducting academic research on carbon neutrality and ESG-related topics, and engaging in communications and collaborations with management departments, research institutions, alumni, and other stakeholders.
This report serves as the debut of CEIBS' carbon disclosure and acts as an affirmation of our firm commitment to the goal of carbon neutrality. As the world grapples with new challenges and opportunities, CEIBS, in line with our commitment to serving the country and addressing the issues of the times, is taking concrete actions to establish a practical paradigm and create a genuine green impact.
Message from the President

Wang Hong
CEIBS President
From the top of the mountain s to the abysses of the deep sea, the intensifying threat of climate change affects every corner of the globe. To address this crisis, the Paris Agreement has underscored the global commitment to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
In response to global climate change, China has pledged to achieve peak carbon by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060, demonstrating its commitment as a great power to build a community of human destiny and drive ecological development. The Chinese government has also rolled out its "1+N" climate policy framework to guide green transformation in economic and social development.
CEIBS, co-founded by the Chinese government and European Union (EU) in 1994, is committed to educating responsible leaders versed in ‘China Depth, Global Breadth’, in line with our motto of ‘Conscientiousness, Innovation and Excellence’. With five campuses across three continents, the school has developed into a top business school in Asia and the world by bridging China and the globe. Over the course of our development, we have steadfastly integrated the concept of sustainable development into education, research, and daily operations, with a focus on energy management and green campuses.
As CEIBS reaches its 30th anniversary, we are tasked with the mission and responsibility of promoting sustainable development and low-carbon transformation in tandem with Chinese national strategies.
This Carbon Information Disclosure Report highlights CEIBS' dedication and commitment to carbon neutrality. We firmly believe that transparent disclosure and open dialogue are not only essential for carbon reduction and low-carbon transformation, but also fundamental to achieving our goals. We will uphold these commitments and strive to create a cleaner and more sustainable world for the future. We also look forward to forging a new chapter in sustainable development together with every member of the CEIBS family!












